
Share 84+ sketch and label chloroplast super hot in.eteachers
Key points: All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. The cell membrane surrounds a cell's cytoplasm, which is a jelly-like substance containing the cell's parts. Cells contain parts called organelles. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell.
Cell components and their functions HubPages
Table of Contents What is a Chloroplast? What are the Key Components of a Chloroplast? Understanding the Structure of a Chloroplast What Function Does the Chloroplast Serve? How Does.

Draw a neat labelled diagram of a chloroplast.
A chloroplast ( / ˈklɔːrəˌplæst, - plɑːst /) [1] [2] is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells.

Diagram of Chloroplast 101 Diagrams
The Chloroplast. Chloroplasts: Theaters for Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis, the process of turning the energy of sunlight into ''food,'' is divided into two basic sets of reactions, known as the light reactions and the Calvin cycle, which uses carbon dioxide.As you study the details in other concepts, refer frequently to the chemical equation of photosynthesis: 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + Light.

Structure Of A Chloroplast stock vector art 477690316 iStock
The main job of chloroplasts is to capture sunlight and turn it into food for the plant. This process is called photosynthesis. Just like how we need food to survive, plants need the food produced by chloroplasts to grow and stay healthy. So, in simple terms, chloroplasts are like the plant's food factories powered by sunlight.

HOW TO DRAW CHLOROPLAST DIAGRAM EASILY? STRUCTURE OF THE CHLOROPLAST YouTube
Figure 1.14. Chloroplasts in the leaf cell of a moss, Plagiomnium affine. (Image: Kristian Peters, CC 3.0 attribute, share alike) Figure 1.15. Internal membrane structure within a chloroplast. (Kelvinsong CC BY-SA 3.0). There are a range of other organelles which are similar to chloroplasts that are used for storage and pigmentation. Figure 1.16.
Chloroplast Definition, Structure, Functions with Diagram
Figure Detail The building and breaking of carbon-based material — from carbon dioxide to complex organic molecules (photosynthesis) then back to carbon dioxide (respiration) — is part of what is.
Photosynthesis storage of solar energy by plants It's a natural universe
Chloroplasts are a type of plastid—a round, oval, or disk-shaped body that is involved in the synthesis and storage of foodstuffs. Chloroplasts are distinguished from other types of plastids by their green colour, which results from the presence of two pigments, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b.

What Is The Function Of The Chloroplast In Plant Cell
What you will learn Structure and function of chloroplast Parts of the chloroplast used in photosynthesis What do pancakes and chloroplasts have in common? The chloroplast is the site of photosynthesis. Part of the photosynthesis reactions occurs in an internal membrane within the organelle.

Chloroplast Definition, Structure & Function (with Diagram) Sciencing
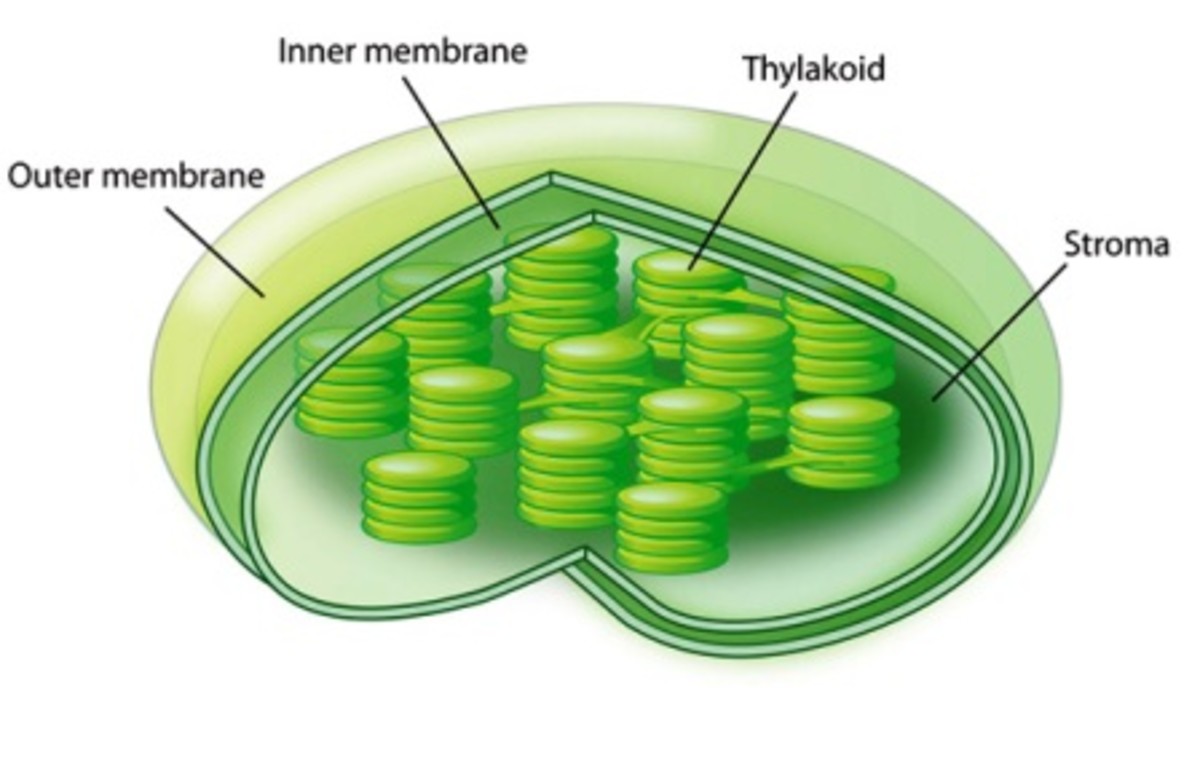
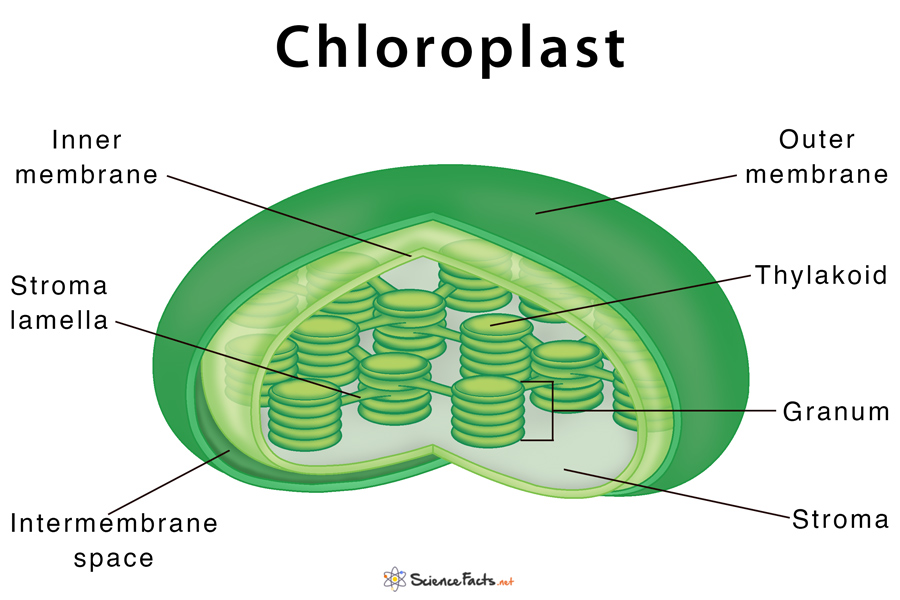
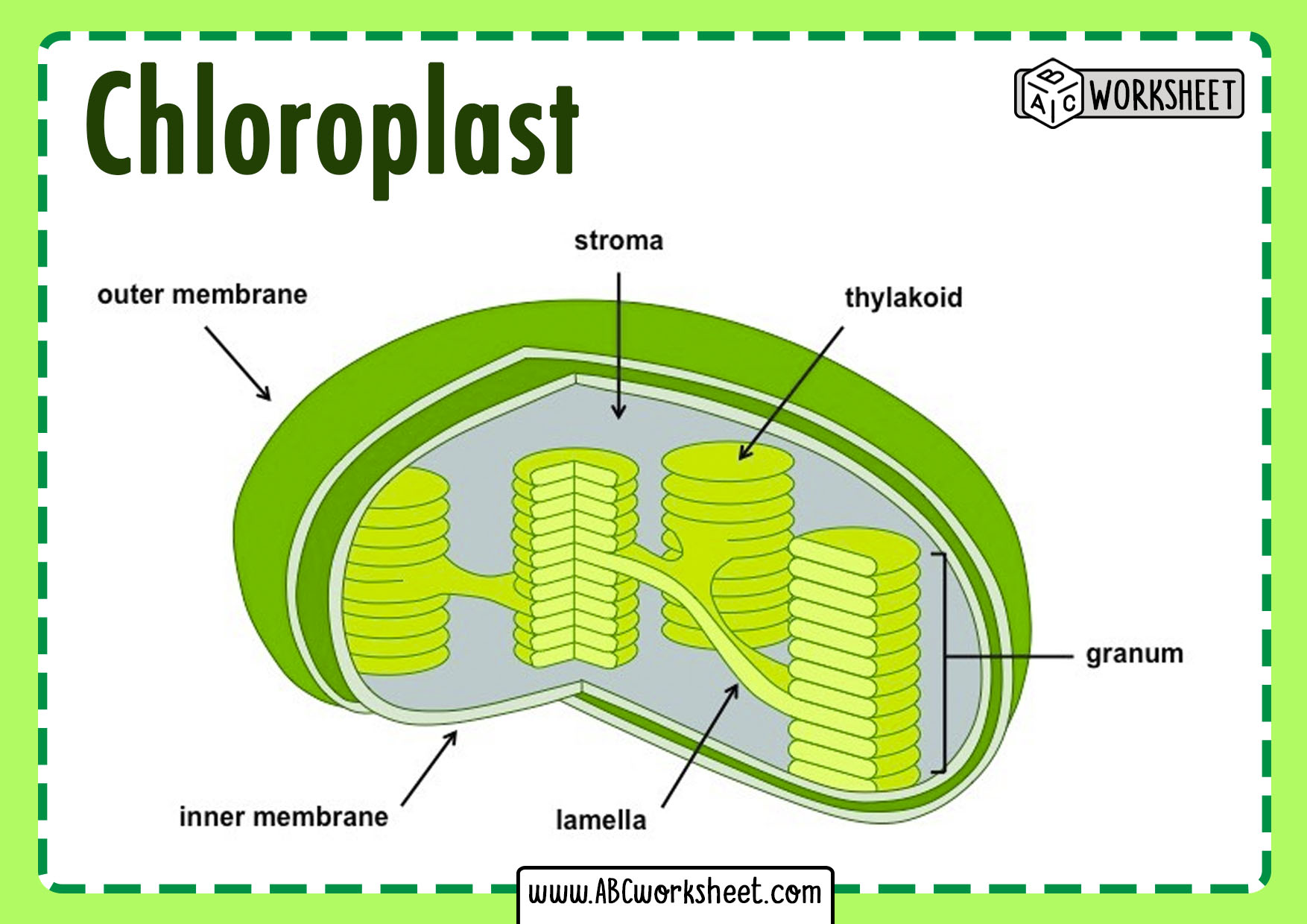
The provided chloroplast diagram offers a visual representation of the chloroplast's structure. It highlights the different components of the chloroplast, such as the outer and inner membranes, thylakoid membrane, stroma, and intermembrane space.. Chloroplast Function Simple: Chloroplasts absorb light energy, transform it into chemical.

What are chloroplasts? Definition, Types and Importance biology AESL
The size of the chloroplast is generally measured at about 5-10 µm in diameter and 2-3 µm in thickness. The chloroplast of cells of polyploid and shade plants are comparatively larger than the chloroplast of cells of diploid and sun plants. From cell to cell, chloroplast's numbers differ from one to another.

Chloroplast Structure, Meaning, Definition, Functions
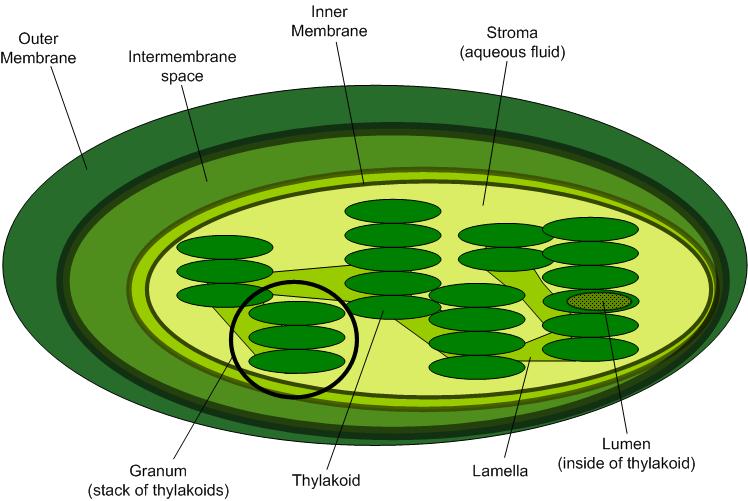
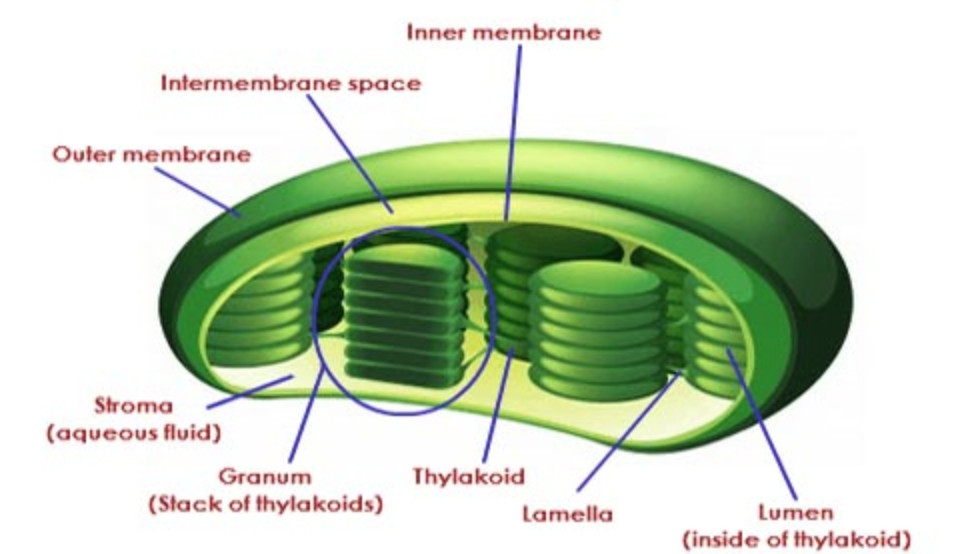
Diagram of a chloroplast Structure Each chloroplast is surrounded by a double walled semi-permeable membrane. These are collectively known as peristromia. In the layered stacks are flat disk-shaped thylakoids. They contain light-absorbing pigments, including chlorophyll and carotenoids, as well as proteins which bind the pigments.
Plastids Class 9, The fundamental unit of lifecell
Figure 10.2.1 10.2. 1: Not all cells of a leaf carry out photosynthesis. Cells within the middle layer of a leaf have chloroplasts, which contain the photosynthetic apparatus. (credit Zephyris; wikimedia) The gas exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen occurs through small, regulated openings called stomata.

FORESTRY LEARNING WHAT IS THE CHLOROPLAST
1. Chloroplasts (Figs. 295-296), responsible for the photosynthesis of the plants, are the characteristic features of the cells of green plants. ADVERTISEMENTS: 2. Around the chloroplast is present a double membrane envelope. 3. Each membrane of chloroplasst is 35 to 50 Å thick. 4. Many dark-coloured grana are present.

Stroma in chloroplast Britannica
Diagram of Chloroplast The diagram of the chloroplast given below represents the chloroplast structure including the different parts of the chloroplast.
Chloroplast Structure
Diagram of Chloroplast The chloroplast diagram below represents the chloroplast structure mentioning the different parts of the chloroplast. The parts of a chloroplast such as the inner membrane, outer membrane, intermembrane space, thylakoid membrane, stroma and lamella can be clearly marked out.